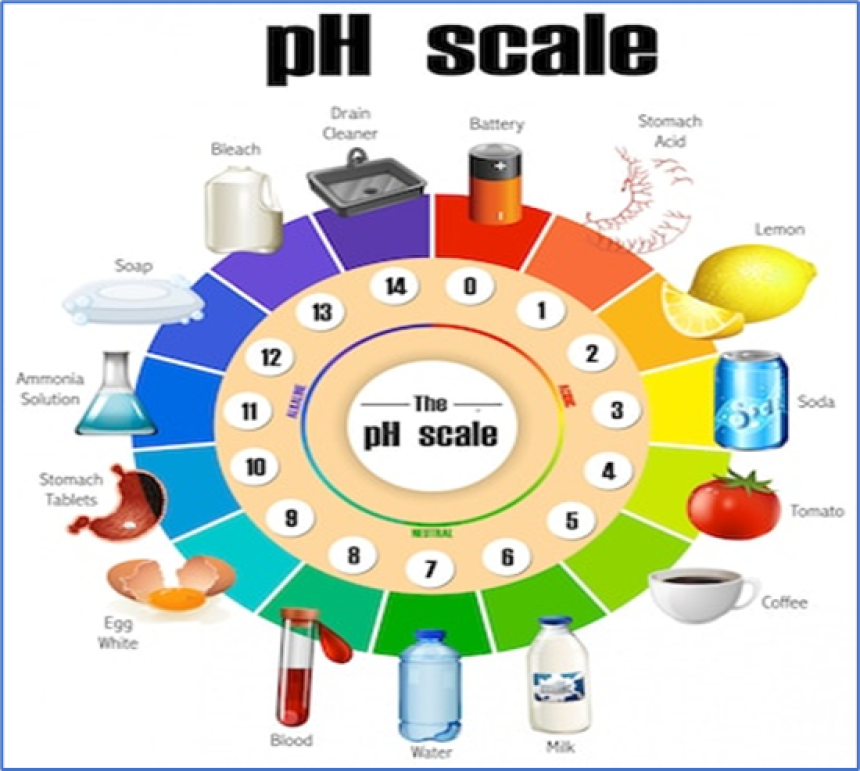
What is ph?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is a logarithmic scale that quantifies the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with lower numbers indicating greater acidity, higher numbers indicating greater alkalinity, and 7 being neutral.
Here's a breakdown of pH values:
- pH 0-6: Acidic
- pH 7: Neutral
- pH 8-14: Alkaline (or basic)
For example:
- Battery acid has a pH of 0, indicating it is highly acidic.
- Pure water has a pH of 7, which is considered neutral.
- Baking soda solution has a pH of around 8, indicating it is slightly alkaline.
It's important to note that the pH scale is logarithmic, which means that each whole pH value represents a tenfold change in acidity or alkalinity. For example, a solution with a pH of 3 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 4.
pH is an important parameter in various fields, including chemistry, biology, agriculture, and environmental science. It has significant implications for chemical reactions, biological processes, and the behavior of substances in different environments. For instance, maintaining the appropriate pH level is crucial in biological systems, as many enzymes and cellular processes function optimally within a specific pH range.





