Hashtags
2 years ago
Hashtags
#what-is-this
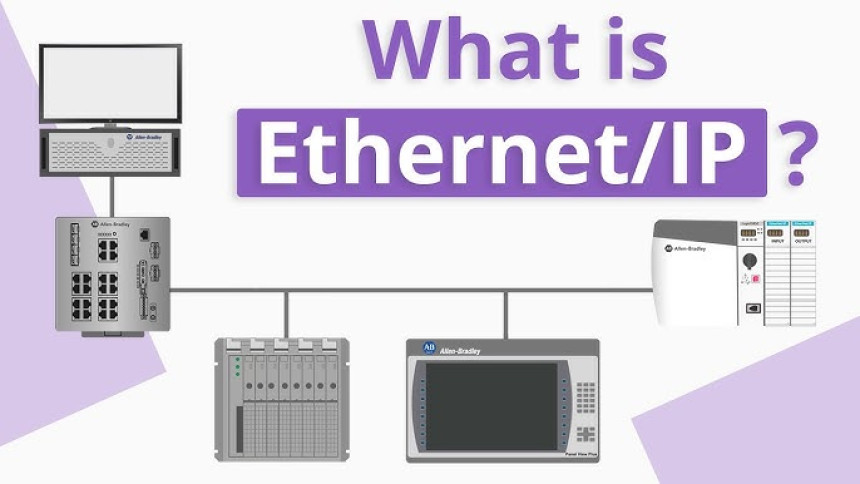
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is a widely used standard for wired computer networking. It defines a set of rules and protocols for transmitting data packets over a wired local area network (LAN). This technology allows devices like computers, printers, and servers to communicate with each other within a local network.
Key features of Ethernet include:

- Wired Connection: Ethernet networks use physical cables, typically made of twisted-pair copper wiring, to transmit data. These cables connect devices to a network switch or router.
- Packet Switching: Data on an Ethernet network is divided into packets, which are discrete units of information. Each packet is individually addressed and routed to its destination. This allows for efficient use of network bandwidth.
- CSMA/CD: Originally, Ethernet used a protocol called Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). This method helped manage data collisions that can occur when multiple devices try to transmit data simultaneously on the network. However, modern Ethernet networks (especially those over switched networks) rarely rely on CSMA/CD.
- Speed and Standards: Ethernet comes in various speeds, commonly referred to as Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps), Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps), 10-Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps), and even faster speeds like 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps. These speeds have evolved over time to accommodate increasing data transfer demands.
- Ethernet Frames: Data transmitted over an Ethernet network is packaged into frames. Each frame contains source and destination MAC (Media Access Control) addresses, payload data, and additional information for error-checking and control.
- Switches and Hubs: Ethernet networks often use network devices like switches or hubs. Switches are intelligent devices that forward data only to the specific device that needs it, while hubs simply broadcast data to all devices on the network.
- Topology: Ethernet networks can be set up in different topologies, including star (devices connect to a central hub or switch), bus (devices are connected in a linear fashion), and mesh (devices are interconnected directly).
- Reliability and Performance: Ethernet is known for its reliability and high performance. It's widely used in both small home networks and large enterprise environments.
- Compatibility and Standardization: Ethernet is a standardized technology, with specifications defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). This ensures that devices from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
- Applications: Ethernet is used for a wide range of applications, including connecting computers to the internet, enabling communication within local networks, and facilitating connections in data centers, industrial automation, and more.
Ethernet has become the dominant wired networking technology, largely replacing older technologies like Token Ring and ARCNET. It's the foundation of most local area networks (LANs) and is also used for connecting devices in wide area networks (WANs) through technologies like Ethernet over Fiber.