Hashtags
2 years ago
Hashtags
#what-is-this
What is Osmosis?
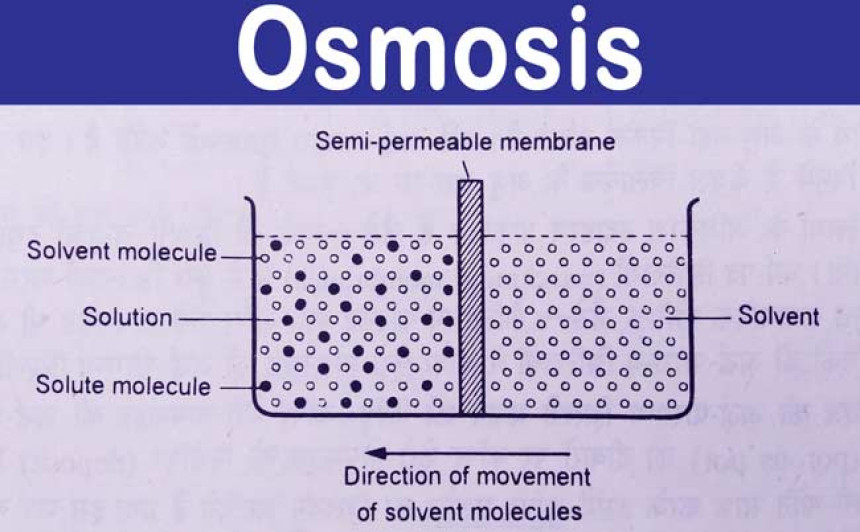
Osmosis is a biological and chemical process that describes the movement of solvent molecules (usually water) across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This movement occurs in order to equalize the concentration of solute on both sides of the membrane.
Here are some key points about osmosis:
- Selective Permeability: Osmosis occurs through a selectively permeable membrane, which means that only certain molecules (in this case, the solvent) can pass through while others are blocked.
- Concentration Gradient: Osmosis always moves solvent molecules from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This creates a concentration gradient.
- Equalizing Concentrations: The ultimate goal of osmosis is to achieve equilibrium, where the concentration of solute is the same on both sides of the membrane.
- Importance in Biological Systems: Osmosis is a critical process in biological systems, particularly in cells. It is essential for maintaining the balance of water and dissolved substances inside and outside of cells. This helps ensure the proper functioning of cells and the overall health of an organism.
- For instance, in animal cells, if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration outside the cell), water will move out of the cell, potentially causing it to shrink or even burst. Conversely, in a hypotonic solution (higher solute concentration inside the cell), water will move into the cell, potentially causing it to swell or burst.
- In plant cells, the cell wall prevents bursting, but the process of osmosis is crucial for maintaining turgor pressure, which helps support the structure of the plant.
- Applications in Chemistry and Industry: Osmosis also has applications in fields like chemistry, where it is used in processes like dialysis. Additionally, it is used in various industrial processes and technologies.
- Reverse Osmosis: This is a related process where pressure is applied to force a solvent to move from a region of higher solute concentration to one of lower solute concentration. It is used in water purification systems to remove contaminants.
Osmosis is a fundamental concept in biology and has broad implications for various fields of science and industry. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids within living organisms and in numerous technological applications.





